THE SCIENCE OF LIGHT
How Light Controls Your Biology
For millions of years, humans evolved under natural light cycles. Modern artificial lighting has disrupted this ancient relationship, with profound consequences for your health, energy, and sleep.
We Evolved Under Natural Light Cycles
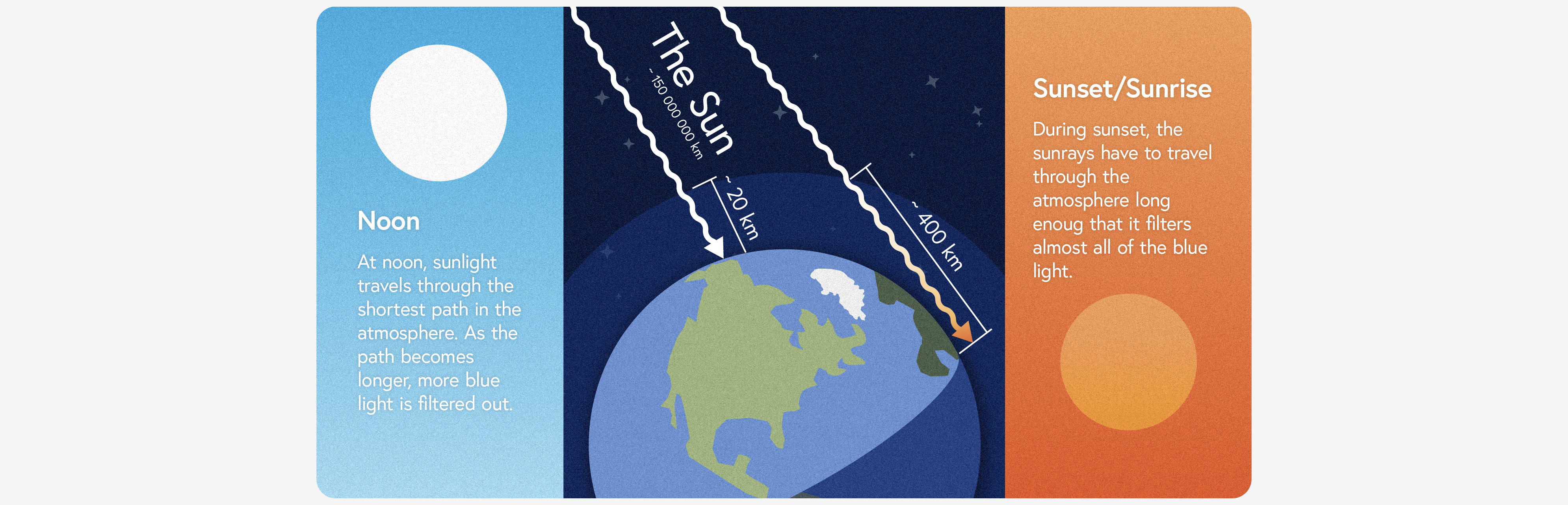
Your biology expects a specific progression of light throughout the day, from bright blue mornings to warm evenings to dark nights.

Bright Days

Warm Evenings

Orange Sunsets

Blueless Nights
It's All About Blue Light
Lots of Blue = Day
Less Blue = Night
Balance Matters
Understanding Your Circadian System
Your Brain Uses Light to Tell Time
Your eyes contain special cells called intrinsic photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) that detect light, specifically blue light around 480nm wavelength.
These cells send signals directly to your suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the master clock in your brain that controls your circadian rhythm.
When blue light hits these cells, your brain interprets it as 'daytime' and suppresses melatonin production while increasing cortisol and alertness.
This system evolved over millions of years when the only light source was the sun during the day and fire at night. We have no mechanism to diferentiate artificial light from sunlight.
The Melatonin Connection
Melatonin is your body's primary sleep hormone, produced by the pineal gland. Its production is directly controlled by light exposure.
Blue light exposure suppresses melatonin production by up to 85%, even at relatively low intensities common in household lighting.
This suppression doesn't just affect sleep onset, it reduces sleep quality, REM sleep duration, and overall restorative benefits.
Red and amber light (above 600nm wavelength) have virtually no effect on melatonin, allowing natural sleep preparation.
Beyond Sleep: Full-Body Impact
Circadian rhythm affects far more than sleep. It controls hormone release, body temperature, digestion, immune function, and cellular repair.
Chronic circadian disruption is linked to increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, depression, and certain cancers.
Your circadian clock influences when you're most alert, creative, and physically capable, misalignment means you're never operating at peak performance.
Studies show shift workers and those with chronic light exposure at night have significantly higher health risks across multiple conditions.
Day/Night Contrast is Everything
Your circadian system doesn't just respond to darkness, it responds to the contrast between bright days and dark nights.
During the Day
- Get bright, blue-rich light exposure (ideally natural sunlight)
- This suppresses melatonin and promotes alertness
- Morning light is especially important for circadian entrainment
At Night
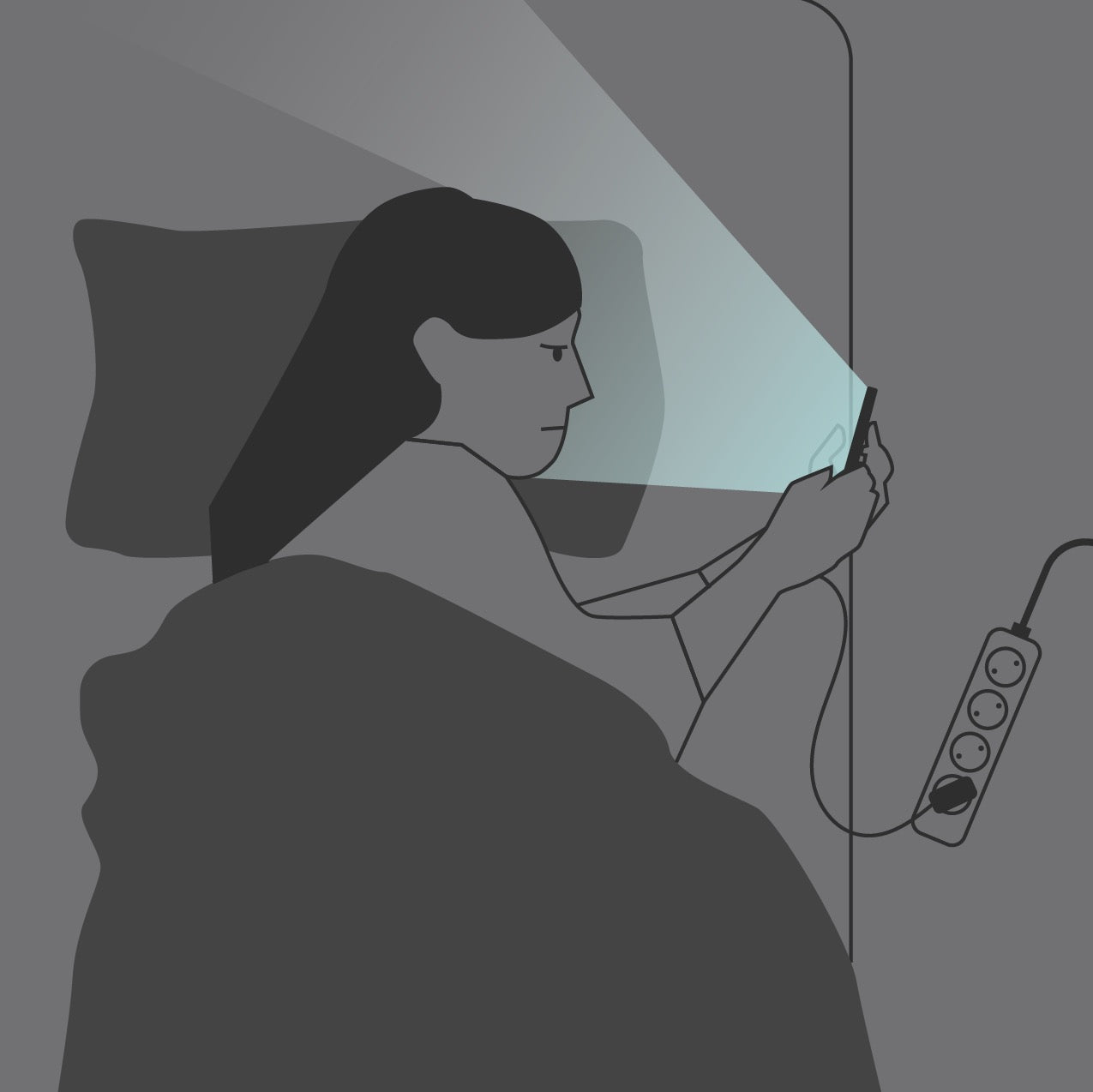
- Eliminate blue light 2 hours before bed
- Use only warm amber or red light in the evening
- Keep your bedroom completely dark for optimal melatonin
Ready to Fix Your Light?

Bright Days
4000K | 520lm

Warm Evenings
2700K | 380lm

Blueless Nights
1100K | 15lm

The Future of Lighting
vitae is here to deliver light optimised for both vision and the circadian system.
Color accuracy, zero flicker, circadian alignment.
Hynek Medřický, inventor of vitae
30+ years in lighting industry, sleep research, and circadian biology.